
They include disorders like Color-blindness and Haemophilia.
 The common sex-linked disorders that are mostly found in humans are mostly recessive. When normal female of F1 is crossed with normal male 50% of males were white-eyed and 50% were red-eyed It shows that the recessive allele is expressed in male only. But all white eyed flies of F2 generation were males only.
The common sex-linked disorders that are mostly found in humans are mostly recessive. When normal female of F1 is crossed with normal male 50% of males were white-eyed and 50% were red-eyed It shows that the recessive allele is expressed in male only. But all white eyed flies of F2 generation were males only. 
F2 generation of it included 3: 1 ratio of red and white-eyed flies. When white-eyed male was mated with a red-eyed female the F1 flies were all red-eyed. In Drosophila, the gene for white eye colour is X linked and recessive to another X-linked, dominant gene for red-eye colour.
Sex linked dominant traits free#
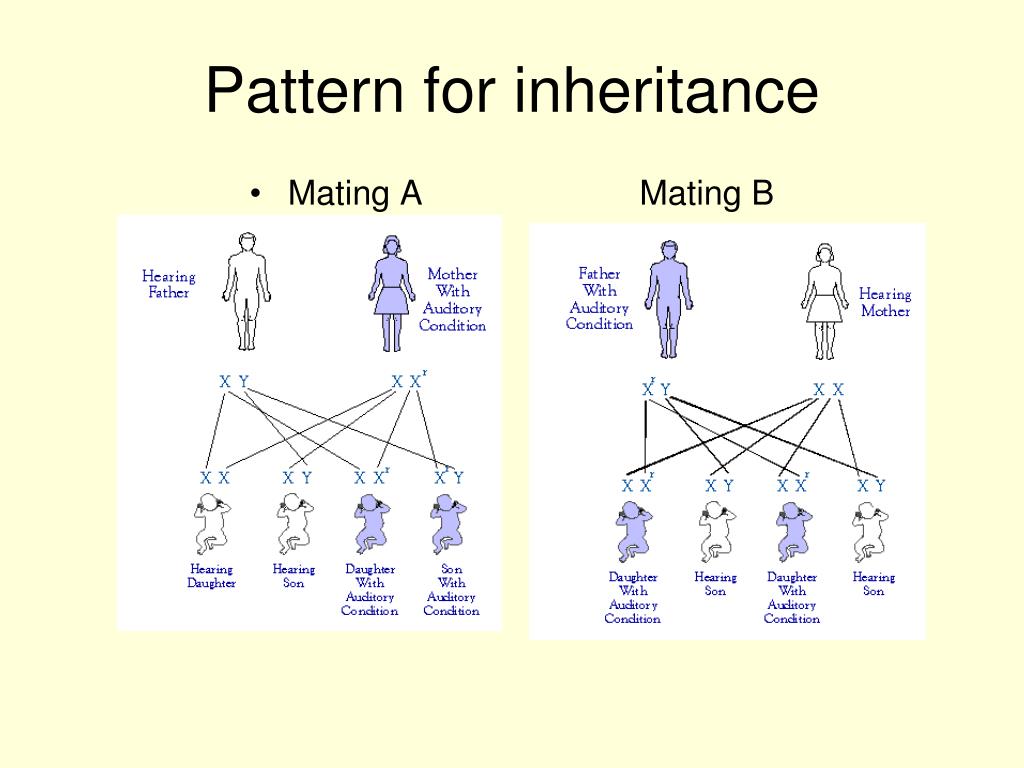
None of the sons of an affected male will inherit the X-linked recessive gene, so not only will they be free of the defective phenotype but they will not pass the gene along to their offspring. Usually none of the offspring of an affected male will be affected, but all his daughters will carry the gene in masked heterozygous condition, so one half of their sons (i.e., grandsons of F1 father) will be affected. This is because an affected female can result only when both mother and father bear the X-linked recessive allele (e.g., XA Xa × Xa Y), whereas an affected male can result when only the mother carries the gene. The X-linked recessive phenotype is usually found more frequently in the male than in the female. In criss-cross inheritance, an X-linked recessive gene is transmitted from P1 male parent (father) to F2 male progeny (grandsons) through its F1 heterozygous females (daughters), which are called carriers) and different F1 and F2 results (ratios) in the reciprocal crosses. The X-linked recessive genes show criss-cross pattern of inheritance. This means haemophilia is much more common in males than in females. However, because males only have one X chromosome, they only need one copy of the haemophilia allele to have the disease. The allele for haemophilia is recessive so two copies are needed for a female to have the disease. Some genetic diseases, are caused by sex linked genes, for example haemophilia. This means females have two alleles for X-linked genes while males only have one. Females have two X chromosomes (XX), while males have one X chromosome and one Y chromosome (XY). These genes are inherited with the X chromosome (from the mother if it is a boy or from either mother or father if it is a girl). Some genes are found on the sex chromosome, X. How we inherit characteristics autosomal dominant where the gene for a trait or condition is dominant, and is on a non-sex chromosome autosomal recessive. Image credit: Genome Research Limited What are sex-linked genes? Illustration to show the inheritance of dominant and recessive alleles for eye colour. For example, the allele for blue eyes is recessive, therefore to have blue eyes you need to have two copies of the 'blue eye' allele. Recessive alleles only show their effect if the individual has two copies of the allele (also known as being homozygous). An example of this is the blood group AB which is the result of codominance of the A and B dominant alleles. 
The resulting characteristic is due to both alleles being expressed equally. If both alleles are dominant, it is called codominance.
For example, the allele for brown eyes is dominant, therefore you only need one copy of the 'brown eye' allele to have brown eyes (although, with two copies you will still have brown eyes).
Dominant alleles show their effect even if the individual only has one copy of the allele (also known as being heterozygous). Alleles can be either dominant or recessive. These different versions of a gene are called alleles. Since human cells carry two copies of each chromosome they have two versions of each gene.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
